本質的に、はんだ付けとろう付けの唯一決定的な違いは温度です。どちらのプロセスも、母材を溶融させることなく充填材を使用して金属を接合しますが、ろう付けは高温(450°C / 840°F以上)で行われるのに対し、はんだ付けはこのしきい値以下で行われる低温プロセスです。この熱における根本的な違いは、接合強度、材料適合性、および適切な用途に直接影響します。
はんだ付けとろう付けの選択は、強度と感度のトレードオフです。ろう付けは非常に強力で構造的な接合を生み出す一方、はんだ付けは熱が低いため、電子機器のようなデリケートで熱に弱い部品にとって唯一実行可能な選択肢となります。
決定要因:温度と充填材
これら2つのプロセスの分類全体は、国際的に認められた1つの温度にかかっています。この単一の変数が、使用される充填材の種類と、結果として生じる接合部の特性を決定します。
450°C (840°F) のしきい値
この特定の温度が正式な境界線です。この点より低い融点を持つ充填材を使用するプロセスはすべてはんだ付けに分類されます。それより高い融点を持つ充填材を使用するプロセスはすべてろう付けに分類されます。
はんだ付け:低温プロセス
はんだ付けでは、通常、錫、鉛、銀、またはその他の低融点元素の合金である充填材、すなわちはんだを使用します。目的は、高強度の機械的結合ではなく、電気的接続を作成することであることが多いです。
ろう付け:高温プロセス
ろう付けでは、銀、銅、ニッケル、アルミニウムなどを多く含む、はるかに高い融点を持つ充填合金を使用します。より高い熱が、毛細管現象と呼ばれるプロセスを通じて、充填材と母材との間のより強力な冶金学的結合を促進します。
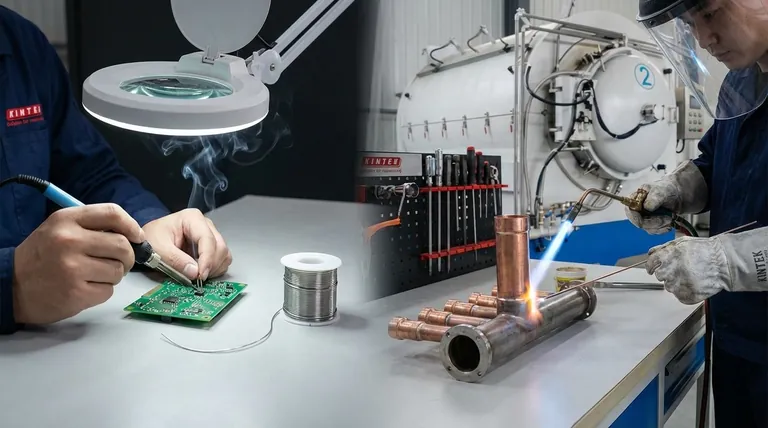
この違いが重要な理由:強度と用途
動作温度の大きな隔たりは、2つの非常に異なる問題に対して2つの非常に異なるツールを生み出します。一方は強度向けに、もう一方は繊細さ向けに作られています。
接合強度:明確な区別
ろう付けされた接合部は、はんだ付けされた接合部よりも劇的に強力です。適切にろう付けされた接合部は、接続されている母材と同じくらい、あるいはそれ以上に強力になることがあります。これにより、かなりの応力や振動に耐えなければならない構造用途に適しています。
対照的に、はんだ付けされた接合部は比較的弱いです。その主な目的は通常、接着と導電性であり、機械的荷重を支えることではありません。
はんだ付けの一般的な用途
はんだ付けの低い熱は、高温によって損傷を受ける可能性のある部品に最適です。最も一般的な用途は、プリント基板(PCB)に部品を取り付けるための電子機器です。また、配管での銅管の接合や、ステンドグラスのような装飾美術にも使用されます。
ろう付けの一般的な用途
ろう付けの強度は、産業製造の主要な要素となっています。自動車産業ではラジエーターやエアコンシステムなどの部品に、HVACでは、工具や重機の部品接合に広く使用されています。
トレードオフを理解する
方法の選択は、単に最も強力なオプションを選ぶだけではありません。ろう付けに必要な高い熱は、考慮すべき重要な制約をもたらします。
熱損傷のリスク
はんだ付けの主な利点は、ろう付けの主な欠点でもあります:熱です。ろう付けの高温は、薄い、デリケートな、または以前に熱処理された母材を容易に損傷または変形させる可能性があり、このプロセスを敏感な用途には不向きにします。
プロセスの複雑さと設備
はんだ付けは一般的にシンプルなプロセスであり、基本的なはんだごてやトーチで達成できることが多いです。ろう付けには、より正確な温度制御とより強力な熱源が必要であり、これにより複雑さとコストが増加する可能性があります。
材料適合性
どちらも異種金属を接合できますが、ろう付けは一般的に汎用性が高いです。高い熱と特殊な充填合金により、鋼と銅、超硬合金と鋼など、非常に幅広い材料間で強力な結合が可能になります。
アプリケーションに合った適切な選択をする
最終的に、選択は特定のプロジェクトの要求に完全に依存します。
- 主な焦点が導電性または熱に弱い部品の接合である場合:低温で適用できるため、はんだ付けが正しい選択です。
- 主な焦点が構造部品の最大の接合強度である場合:ろう付けが優れており、接合される材料と同じくらい強力な結合を生成します。
- 主な焦点が異種金属または高強度金属の接合である場合:ろう付けは、困難な材料の組み合わせに対して、より堅牢で信頼性の高いソリューションを提供します。
熱、強度、部品の感度というこの根本的なトレードオフを理解することが、作業に適切な接合プロセスを選択するための鍵となります。
要約表:
| 特徴 | はんだ付け | ろう付け |
|---|---|---|
| プロセス温度 | 450°C (840°F)未満 | 450°C (840°F)以上 |
| 接合強度 | 低い(接着/電気用) | 高い(構造用、母材と同等の強度) |
| 主な用途 | 電子機器、配管、デリケートな部品 | 自動車、HVAC、重機 |
| 熱感度 | 熱に弱い部品に最適 | デリケートな材料を損傷するリスクあり |
金属接合用途に関する専門家のアドバイスが必要ですか?完璧なはんだ付けまたはろう付けの結果を達成するには、適切な装置が不可欠です。KINTEKは、あらゆる熱処理ニーズに対応する高性能ラボ機器と消耗品を専門としています。当社のソリューションは、デリケートな電子アセンブリと堅牢な産業用ろう付けの両方で、正確な温度制御と信頼性の高い性能を保証します。
お客様の特定の要件に最適な機器の選択を当社の専門家がお手伝いします。
今すぐお問い合わせください KINTEKがお客様のラボの能力と効率をどのように向上させることができるかについてご相談ください!
ビジュアルガイド

関連製品
- 真空熱処理焼結ろう付け炉
- 高温用途向け熱蒸着タングステン線
- 真空熱処理・モリブデン線焼結炉(真空焼結用)
- エンジニアリング先進ファインセラミックス加工用カスタムメイドアルミナジルコニア特殊形状セラミックプレート
- 真空熱間プレス炉 加熱真空プレス機 チューブ炉

























