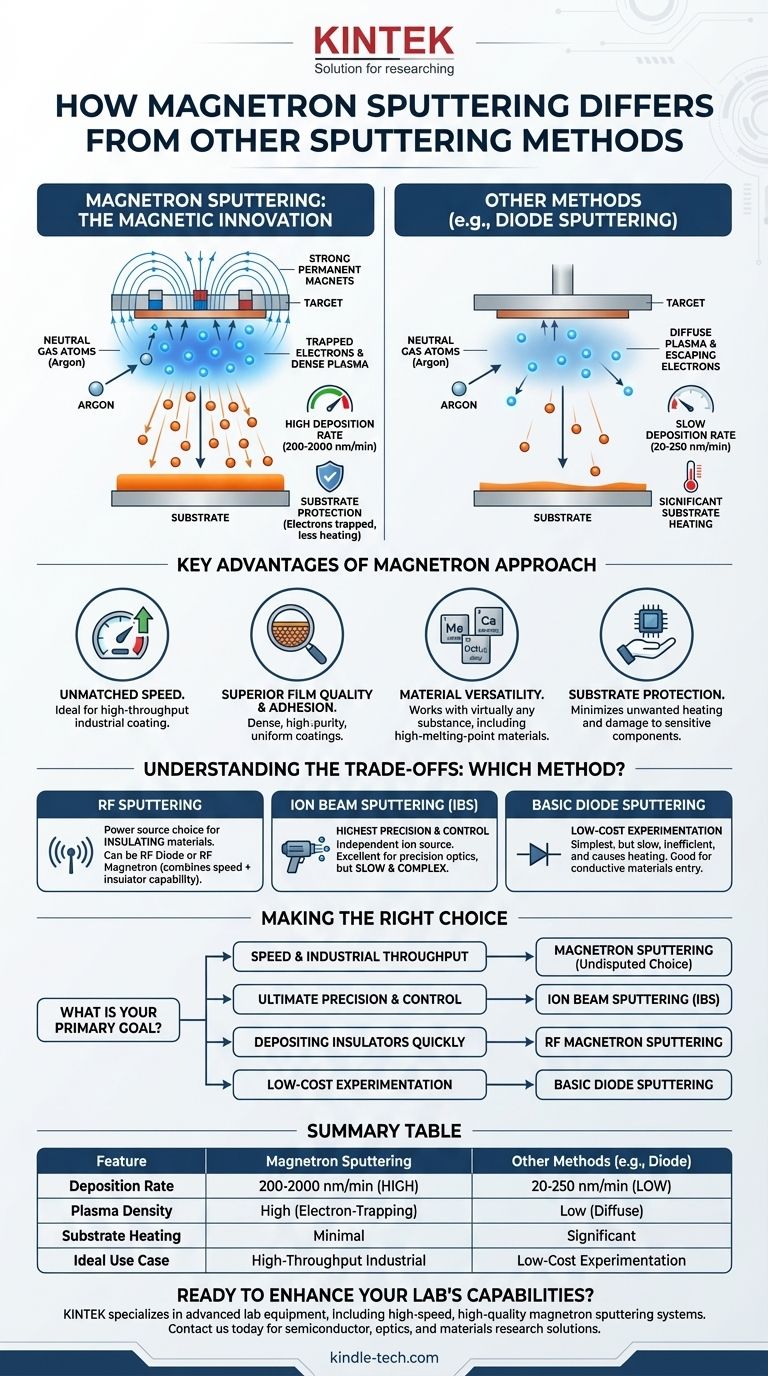
根本的な違いは、磁場の使用です。マグネトロンスパッタリングでは、ターゲット材の背後に強力な磁石を戦略的に配置し、ターゲットのすぐ前で電子を密度の高いプラズマ雲に閉じ込めます。この集中的なプラズマは、他のスパッタリング方法よりもはるかに激しくターゲットを衝突するため、成膜速度が大幅に向上します(多くの場合、1桁速くなります)。
すべてのスパッタリング方法が薄膜作製のためにターゲットから原子を叩き出しますが、マグネトロンスパッタリングにおける磁場の使用が鍵となる革新です。この単一の変化により、成膜プロセスの速度と効率が劇的に向上し、ほとんどの産業用途で主流の技術としての地位を確立しています。

コアメカニズム:磁石がいかにスパッタリングに革命をもたらすか
違いを理解するためには、まず基本的なスパッタリングの核となる課題を見る必要があります。このプロセスは、イオン化されたガスであるプラズマを利用して、イオンを生成し、そのイオンがソース材料、すなわち「ターゲット」に衝突するようにします。
基本的なスパッタリングの問題点
単純なダイオードスパッタリングシステムでは、プラズマは拡散しており非効率的です。スパッタリングを行うイオンの生成に不可欠な電子は、自由に逃げることができ、基板に衝突して損傷や加熱を引き起こす可能性があります。その結果、成膜速度が遅くなります。
マグネトロンによる解決策:電子の閉じ込め
マグネトロンスパッタリングでは、ターゲットのすぐ背後に強力な磁場が導入されます。この磁場は電場に対して垂直であり、高エネルギーの二次電子をらせん状の軌道に強制的に閉じ込め、ターゲット表面の近くに効果的に閉じ込めます。これにより、電子が基板に到達するのを防ぎ、プラズマ内での移動経路が劇的に長くなります。
結果:高密度のプラズマ
電子が閉じ込められ、はるかに長く移動するため、中性ガス原子(アルゴンなど)とのイオン化イベントが大幅に増加します。これにより、ターゲットのすぐ前に局在する、はるかに高密度で強力なプラズマが生成されます。
この高密度プラズマは、ターゲットに継続的に衝突する大量のイオンを生成し、非常に高い速度で材料を叩き出します。
マグネトロンアプローチの主な利点
磁場の使用は、より基本的なスパッタリング方法と比較して、いくつかの明確で強力な利点をもたらします。
比類のない成膜速度
主な利点は、コーティング率の劇的な向上です。参照データが示すように、マグネトロンスパッタリングは、標準的なRFスパッタリングで一般的な 20~250 nm/min に対し、200~2000 nm/min の速度を達成できます。これにより、スループットが重要な産業規模の生産に理想的です。
優れた膜質と密着性
スパッタリングされた原子は、蒸着された材料よりも本質的に高い運動エネルギーを持っており、優れた密着性を持つ高密度膜の形成に役立ちます。マグネトロンスパッタリングは、均一なコーティングを生成する安定した高純度プロセスを維持することで、これを強化します。
材料の多様性
スパッタリングは物理的なプロセスであり、ソース材料を溶かす必要がないため、事実上あらゆる物質に使用できます。これには、金属、合金、セラミックス、熱蒸着では堆積不可能な超高温融点材料が含まれます。
基板の保護
電子をターゲットの近くに閉じ込めることにより、マグネトロンスパッタリングは電子が基板に衝突するのを防ぎます。これにより、特にプラスチックや電子部品などの敏感な基板にとって重要な、不要な加熱や潜在的な放射線損傷を最小限に抑えます。
トレードオフの理解:マグネトロンと他の方法の比較
マグネトロンスパッタリングは多くの用途で優れた技術ですが、唯一の選択肢ではありません。選択は、精度、材料、コストに関する特定の目標によって異なります。
基本的なダイオードスパッタリングとの比較
ダイオードスパッタリングは最も単純な形態であり、磁気閉じ込めがありません。これは遅く、非効率的で、かなりの基板加熱を引き起こします。マグネトロンスパッタリングは、特に速度と膜質に関して、ほぼすべての指標において直接的かつ大幅な改善です。
RFスパッタリングとの比較
高周波(RF)スパッタリングは、電源の選択という点で、別個の方法というよりも電源の選択肢です。絶縁体(誘電体)材料をスパッタリングするには、RFが必要です。RFダイオードスパッタリングまたはRFマグネトロンスパッタリングのいずれかを選択できます。RF電源とマグネトロンソースを組み合わせることで、マグネトロンの速度と絶縁体を堆積させる能力の両方を得ることができます。
イオンビームスパッタリング(IBS)との比較
イオンビームスパッタリングは、最も高度な制御を提供します。IBSでは、イオン源がターゲットから分離されており、イオンエネルギー、角度、フラックスを独立して制御できます。これにより、精密光学などのハイエンド用途向けに、極めて高密度で平滑で応力が制御された膜を作成するための比類のない精度が得られます。
トレードオフは速度とコストです。IBSはマグネトロンスパッタリングよりも大幅に遅く、複雑であるため、大量生産には適していません。
アプリケーションに最適な選択をする
適切なスパッタリング方法を選択するには、その技術の強みをプロジェクトの主な目的に合わせる必要があります。
- 主な焦点が速度と産業スループットの場合:マグネトロンスパッタリングは、高い成膜速度とコスト効率から、議論の余地のない選択肢です。
- 主な焦点が究極の膜密度と精密制御の場合:イオンビームスパッタリング(IBS)は、敏感な光学コーティングや高度な半導体膜に必要な微調整を提供します。
- 迅速に絶縁材料を堆積させることが主な焦点の場合:RFマグネトロンスパッタリングは、RFの能力とマグネトロンの速度を組み合わせ、両方の長所を提供します。
- 主な焦点が導電性材料に関する低コストの実験の場合:単純なDCダイオードスパッタリングセットアップは、遅いものの、実行可能な入門点となります。
結局のところ、磁場の役割を理解することが、その仕事に最適なツールを選択できるようにします。
要約表:
| 特徴 | マグネトロンスパッタリング | 他の方法(例:ダイオードスパッタリング) |
|---|---|---|
| 成膜速度 | 200-2000 nm/min | 20-250 nm/min |
| プラズマ密度 | 高(電子閉じ込め) | 低(拡散) |
| 基板加熱 | 最小限 | 顕著 |
| 理想的な用途 | 高スループットの産業用コーティング | 低コストの実験 |
研究室の薄膜能力を向上させる準備はできましたか? KINTEKは、高い成膜速度と優れた膜質を実現するように設計されたマグネトロンスパッタリングシステムを含む、高度なラボ機器を専門としています。半導体製造、光学、材料研究のいずれに従事している場合でも、当社のソリューションは精度と効率を提供します。当社の専門家に今すぐお問い合わせいただき、お客様の研究室のニーズに最適なスパッタリングシステムを見つけてください!
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
- RF PECVDシステム RFプラズマエッチング装置
- 化学気相成長CVD装置システム チャンバースライド式 PECVD管状炉 液体気化器付き PECVDマシン
- 真空ステーション付き分割チャンバーCVDチューブ炉 化学蒸着システム装置
- 高真空システム用 304/316 ステンレス鋼真空ボールバルブ ストップバルブ
- 真空熱間プレス炉 加熱真空プレス機 チューブ炉



















