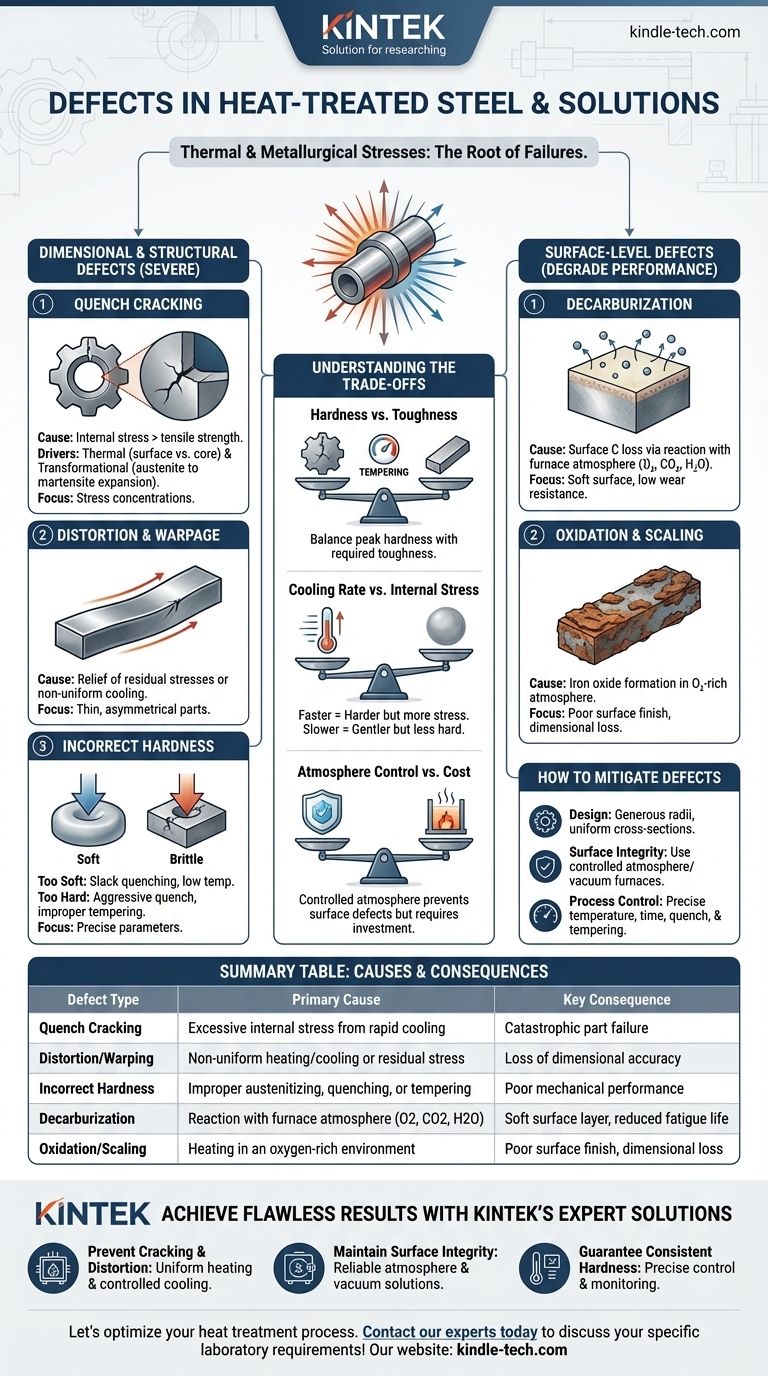
熱処理された鋼の欠陥は、主に加熱および急速冷却中に導入される莫大な熱的および冶金的応力によって引き起こされます。最も一般的な欠陥は、割れ、歪み(反り)、脱炭やスケールなどの望ましくない表面変化、および目標とする硬度や微細構造を達成できないことです。これらの故障はランダムに発生するのではなく、不適切に制御されたプロセスパラメータの直接的な結果です。
熱処理欠陥は、熱応力、相変態、および大気中の化学反応の予測可能な結果です。それらを防止するには、温度変化の速度、炉の雰囲気、および設計段階からの部品の形状を厳密に制御することが重要です。
寸法および構造上の故障
最も深刻な欠陥は、コンポーネントの機械的完全性と寸法精度を損ない、多くの場合、使用不能にします。
焼入れ割れ
焼入れ割れは、最も重大な熱処理欠陥です。これは、焼入れ時の内部応力が材料の究極引張強度を超えるときに発生します。
これは、表面がコアよりもはるかに速く冷却されることによる熱応力と、オーステナイトが脆いマルテンサイトに変態する際に発生する膨張による変態応力という2つの主要な力によって引き起こされます。
亀裂は通常、鋭い角、キー溝、または部品の断面の急激な変化などの応力集中点から発生します。
歪みと反り
歪みは、熱処理中に発生する部品のサイズまたは形状の不可逆的な変化です。
これは、以前の製造工程(機械加工など)で付与された残留応力の解放、または不均一な加熱および冷却によって引き起こされることがよくあります。薄い、長い、または非対称な部品は、特に反りの影響を受けやすいです。
不適切な硬度
適切な硬度を達成することが主な目標であることが多く、ここでの失敗はいくつかの要因による可能性があります。
軟らかすぎる部品は、オーステナイト化温度または時間が不十分であったり、鋼の焼入れ性に対して焼入れが遅すぎた(焼入れ不足として知られる)場合に発生する可能性があります。
逆に、硬すぎてもろい部品は、過度に激しい焼入れ、またはより一般的には、硬化後の不適切または省略された焼戻し工程の結果であることがよくあります。

表面レベルの欠陥
これらの欠陥は鋼の表面を劣化させ、高い耐摩耗性や疲労強度を必要とする用途での性能を損ないます。
脱炭
脱炭は、鋼の表面からの炭素の損失です。炭素は鋼の硬度を担う主要な元素であるため、これは重大な問題です。
これは、高温で鋼と炉の雰囲気(酸素、二酸化炭素、水蒸気)との間の化学反応によって引き起こされます。結果として、耐摩耗性と疲労寿命を大幅に低下させる軟らかく弱い表面層が形成されます。
酸化とスケール
酸化は、酸素が豊富な雰囲気で加熱されたときに、部品の表面に酸化鉄(スケール)の層が形成されることです。
このスケールは、表面仕上げの悪化と寸法精度の損失を引き起こします。また、部品を断熱し、不均一な焼入れを引き起こし、焼入れ割れのようなより深刻な根本的な欠陥を隠す可能性があります。
トレードオフの理解
熱処理プロセスを選択する際には、常に相反する要因のバランスを取る必要があります。これらのトレードオフを理解することが、欠陥を防ぐ鍵となります。
硬度 vs. 靭性
熱処理における基本的なトレードオフは、焼入れのように極端な硬度を生み出すプロセスは、脆い微細構造(未焼戻しマルテンサイト)も生み出すということです。
焼戻しは、この脆さと内部応力を低減し、靭性を付与する焼入れ後の重要な工程です。ただし、このプロセスはピーク硬度も低下させます。その技術は、用途に必要な正確なバランスを見つけることにあります。
冷却速度 vs. 内部応力
冷却速度が速いほど、特に低合金鋼において、完全な硬度を達成するのに効果的です。
しかし、急速な焼入れ(例:水や塩水を使用)は、途方もない熱勾配と内部応力を発生させ、歪みや割れのリスクを劇的に高めます。より遅い焼入れ(例:油やガスを使用)は穏やかですが、最大の硬度を達成できない場合があります。
雰囲気制御 vs. コスト
制御された雰囲気(真空、窒素、アルゴンなど)を使用すると、脱炭と酸化を完全に防ぎ、きれいで明るい部品が得られます。
ただし、これらのプロセスは、開放炉での加熱と比較して、より洗練された高価な設備を必要とします。コストは、部品の表面要件によって正当化されなければなりません。
熱処理欠陥を軽減する方法
欠陥を防ぐには、設計、材料選択、および精密なプロセス制御に焦点を当てた体系的なアプローチが必要です。
- 割れや歪みの防止が主な焦点である場合:大きな半径と均一な断面を持つ部品を設計し、鋼の焼入れ性に適した穏やかな焼入れ媒体を選択してください。
- 表面の完全性の維持が主な焦点である場合:脱炭とスケールを防ぐために、制御雰囲気炉(例:真空、不活性ガス)または保護コーティングを利用してください。
- 一貫した硬度の達成が主な焦点である場合:オーステナイト化温度、保持時間、および焼入れ攪拌の精密な制御を確保し、常に適切な焼戻しサイクルを行ってください。
成功する熱処理は、設計における先見性と実行における精度が部品の最終的な品質を決定する、制御されたエンジニアリングプロセスです。
要約表:
| 欠陥の種類 | 主な原因 | 主な結果 |
|---|---|---|
| 焼入れ割れ | 急速冷却による過剰な内部応力 | 壊滅的な部品の故障 |
| 歪み/反り | 不均一な加熱/冷却または残留応力 | 寸法精度の損失 |
| 不適切な硬度 | 不適切なオーステナイト化、焼入れ、または焼戻し | 劣悪な機械的性能 |
| 脱炭 | 炉雰囲気(O2、CO2、H2O)との反応 | 軟らかい表面層、疲労寿命の短縮 |
| 酸化/スケール | 酸素が豊富な環境での加熱 | 劣悪な表面仕上げ、寸法損失 |
KINTEKの専門ソリューションで完璧な結果を達成
高価な熱処理欠陥を排除し、鋼部品が硬度、耐久性、寸法精度の最高基準を満たしていることを確認してください。KINTEKは、プレミアムな実験装置と消耗品を専門とし、熱処理を完璧にするために研究室が必要とする精密な炉、雰囲気制御システム、および専門家によるサポートを提供します。
KINTEKがお手伝いすること:
- 割れと歪みの防止:均一な加熱と制御された冷却のために設計された装置を使用。
- 表面の完全性の維持:信頼性の高い雰囲気制御および真空炉ソリューションを通じて。
- 一貫した硬度の保証:精密な温度制御および監視ツールを使用。
熱処理プロセスを最適化しましょう。今すぐ専門家にお問い合わせください。お客様の特定の実験室要件についてご相談ください!
ビジュアルガイド