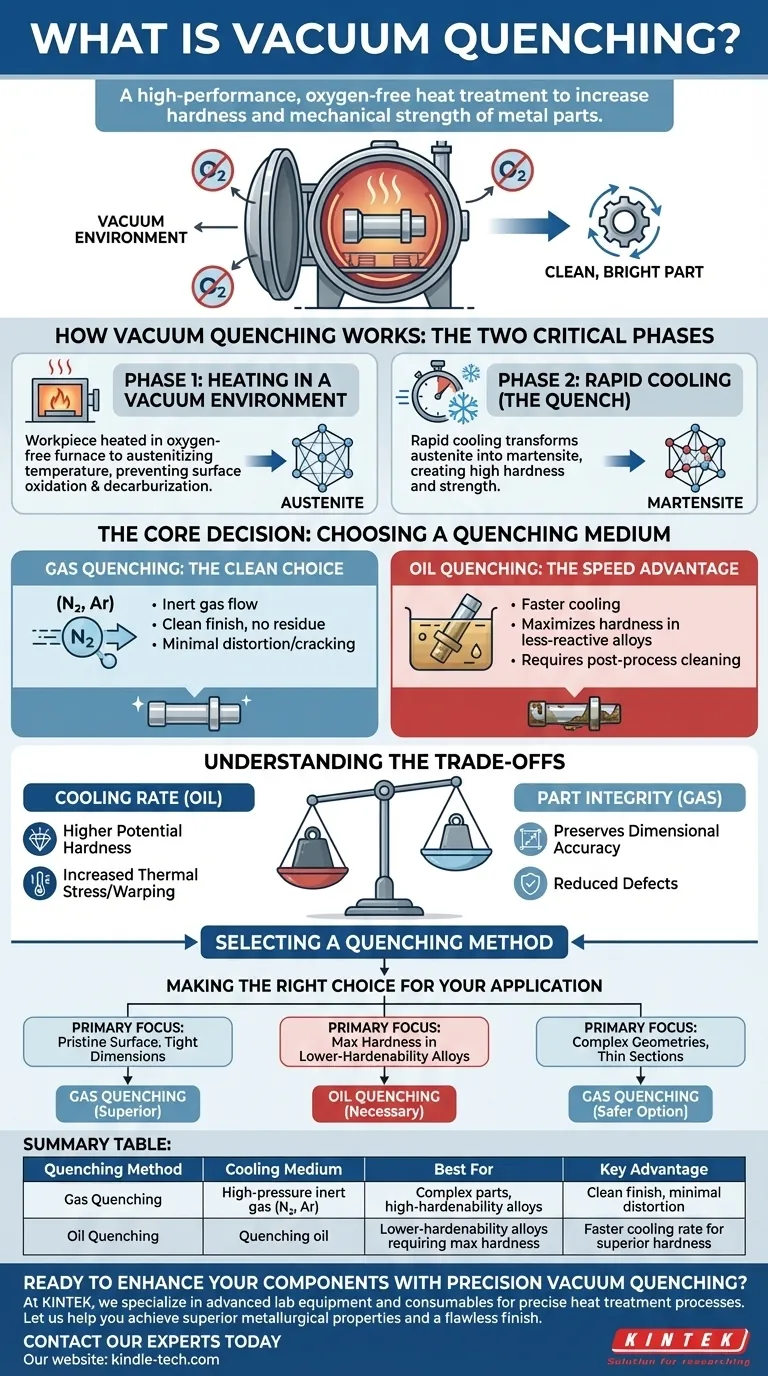
真空焼入れは、金属部品の硬度と機械的強度を向上させるために使用される高性能熱処理プロセスです。真空炉内で材料を特定の温度まで加熱し、保持した後、制御された媒体で急速に冷却し、望ましい冶金組織を固定します。このプロセス全体は酸素なしで行われるため、表面酸化を防ぎ、クリーンで明るい部品が得られます。
要するに、真空焼入れは、金属の内部構造を最大限の硬度に変えることと、スケールや変色などの表面欠陥を防ぐために無欠陥環境で行うこと、という2つの目標を同時に達成することです。このプロセスにおける重要な決定は、冷却速度と部品の完全性のバランスを決定する適切な冷却媒体(ガスまたは油)を選択することです。

真空焼入れの仕組み:2つの重要なフェーズ
このプロセスは、加熱と焼入れという2つの明確で同様に重要な段階に分けることができます。真空環境は、この技術を非常に効果的にしている共通の要素です。
フェーズ1:真空環境下での加熱
最初のステップは、加工物を真空炉に入れることです。炉内は排気され、酸素やその他の反応性ガスが除去されます。
その後、部品はオーステナイト化温度、つまり結晶構造がオーステナイトとして知られる相に変化する特定の点まで加熱されます。
この制御された酸素のない雰囲気は、従来の雰囲気炉で一般的な問題である酸化と脱炭(表面からの炭素の損失)を完全に防ぐため、非常に重要です。
フェーズ2:急速冷却(焼入れ)
材料が完全にオーステナイトに変態した後、急速に冷却する必要があります。この急速な冷却、すなわち「焼入れ」は、オーステナイト構造がより柔らかい加熱前の状態に戻るのを防ぎます。
代わりに、非常に硬く脆い結晶構造であるマルテンサイトへの変態を強制します。焼入れ部品に高い硬度と強度を与えるのは、このマルテンサイト組織です。
焼入れの速度は極めて重要であり、使用される冷却媒体によって決まります。
核心的な決定:焼入れ媒体の選択
冷却媒体の選択は、真空焼入れにおいて最も重要な変数であり、部品の最終的な特性に直接影響します。
ガス焼入れ:クリーンな選択肢
真空ガス焼入れでは、加熱された部品に高圧の不活性ガス(通常は窒素またはアルゴン)を炉内に導入して冷却します。
この方法は非常にクリーンで、部品の表面に残留物を残しません。部品は炉から明るく光沢のある状態で取り出され、後処理の洗浄なしに使用できます。
ガス焼入れは、より均一で穏やかな冷却を提供するため、特に複雑な形状や薄いセクションの部品において、部品の歪みや亀裂のリスクを大幅に低減します。
油焼入れ:スピードの利点
硬化性が低い一部の鋼合金の場合、ガス焼入れでは完全なマルテンサイト変態を達成するのに十分な速度ではありません。これらの材料には真空油焼入れが必要です。
このプロセスでは、加熱された部品は真空加熱チャンバーから、焼入れ油が充填された統合された密閉チャンバーに移されます。
油はガスよりもはるかに速く熱を奪うため、反応性の低い合金でも最大の硬度を達成できます。トレードオフとして、処理後に油の残留物を取り除くために部品を徹底的に洗浄する必要があります。
トレードオフの理解
焼入れ方法の選択は、競合する優先順位のバランスを取る必要があります。選択は常に一連の工学的なトレードオフを伴います。
冷却速度 vs. 部品の完全性
より速い焼入れ(油)はより高い潜在的な硬度をもたらしますが、より大きな熱応力も誘発します。これにより、ワークピースの反り、歪み、さらには微小な亀裂のリスクが増加します。
より遅く、より制御された焼入れ(ガス)は部品に対して穏やかであり、寸法精度を維持し、欠陥の可能性を減らします。
清浄度 vs. プロセスの複雑さ
ガス焼入れは、単一ステップのクリーンなプロセスです。部品は炉から出た時点で完了です。
油焼入れは本質的に汚れており、追加的で、しばしば時間のかかる洗浄工程が必要です。これは、製造ワークフロー全体に運用の複雑さとコストを追加します。
材料の適合性
選択は材料自体によって決定されることがよくあります。特定の工具鋼のような高硬化性合金は、ガスで正常に硬化させることができます。
しかし、多くの一般的な構造鋼やベアリング鋼は、指定された硬度要件を満たすために、より積極的な油の冷却速度を必要とします。
アプリケーションに最適な方法の選択
正しい方法を選択するには、部品にとって最も重要な結果を明確に定義する必要があります。
- 最優先事項が完璧な表面仕上げと厳密な寸法安定性である場合: ガス焼入れは、洗浄の必要性をなくし、歪みを最小限に抑えるため、優れた選択肢です。
- 硬化性が低い合金で最大の硬度を達成することが最優先事項である場合: より速く積極的な冷却速度のため、油焼入れが必要になることがよくあります。
- プロジェクトに複雑な形状、鋭い角、または薄い断面が含まれる場合: ガス焼入れは、より制御された均一な冷却プロセスを提供するため、欠陥を防ぐためのより安全なオプションです。
これらの基本原則を理解することで、材料の冶金学的ニーズとプロジェクトの最終的な品質基準の両方を満たす正確な真空焼入れ方法を選択できます。
要約表:
| 焼入れ方法 | 冷却媒体 | 最適用途 | 主な利点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ガス焼入れ | 高圧不活性ガス(N₂、Ar) | 複雑な部品、高硬化性合金 | クリーンな仕上げ、歪みの最小化 |
| 油焼入れ | 焼入れ油 | 最大の硬度を必要とする低硬化性合金 | 優れた硬度のためのより速い冷却速度 |
精密な真空焼入れでコンポーネントの性能を向上させる準備はできていますか?
KINTEKでは、正確な熱処理プロセス向けの高度なラボ機器と消耗品の提供を専門としています。ガス焼入れのクリーンで歪みのない結果であれ、油焼入れで達成される最大の硬度であれ、当社のソリューションはお客様の研究所の特定の材料と品質基準を満たすように調整されています。
優れた冶金特性と完璧な仕上げを実現するために、私たちがお手伝いします。 当社の専門家に今すぐお問い合わせいただき、プロジェクトの要件についてご相談の上、お客様のニーズに合った適切な真空焼入れソリューションを見つけてください。
ビジュアルガイド