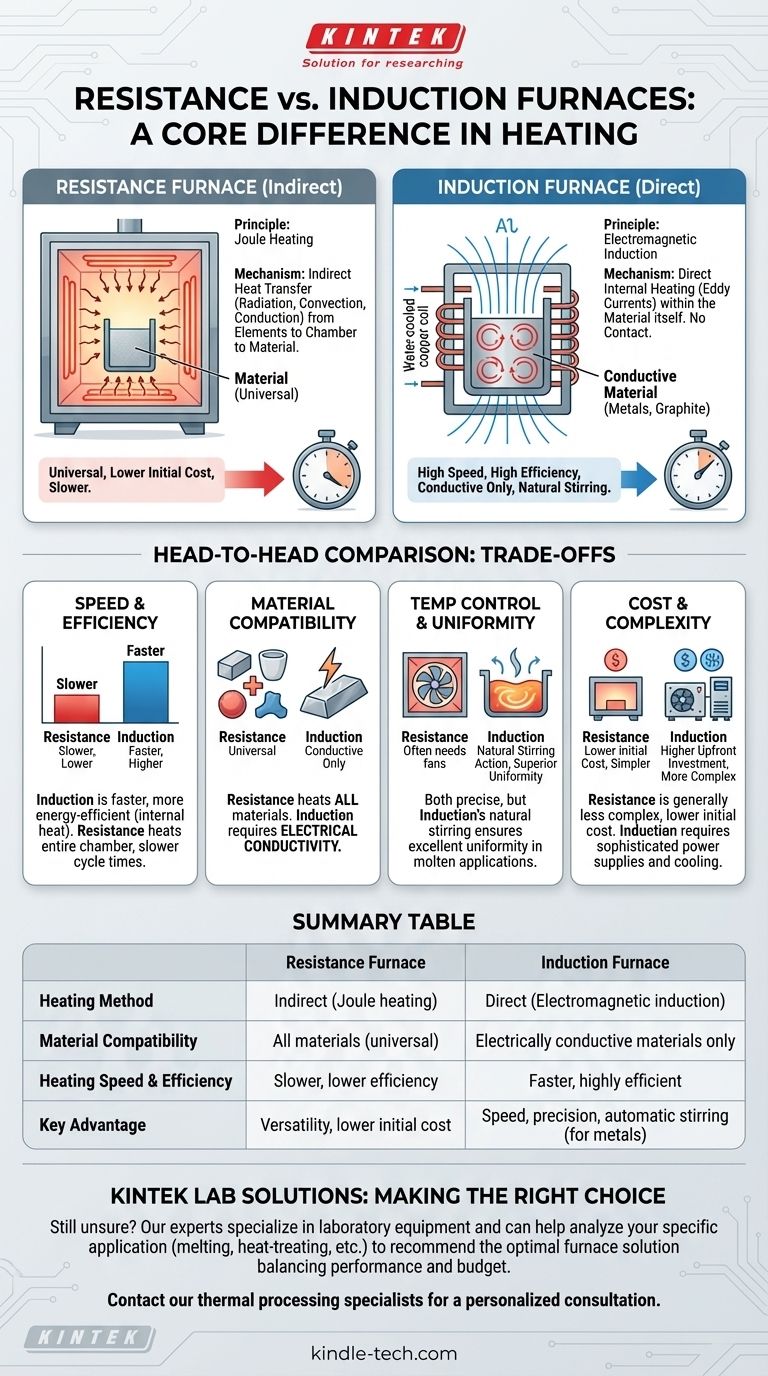
抵抗炉と誘導炉の根本的な違いは、その加熱方法にあります。抵抗炉は、従来のオーブンのように、発熱体が熱くなり、間接的に材料に熱を伝えます。対照的に、誘導炉は電磁場を利用して、導電性材料の内部で直接熱を発生させ、物理的な接触はありません。
これら2つの技術のどちらを選択するかは、汎用性と効率のトレードオフにかかっています。抵抗炉はあらゆる材料を加熱するための普遍的なツールである一方、誘導炉は金属のような導電性材料に特化した、高速で高効率な専門ツールです。
抵抗炉の仕組み
抵抗炉は、最も一般的でシンプルなタイプの電気炉であり、トースターや電気コンロを使ったことがある人にはおなじみの原理で動作します。
原理:ジュール熱
そのメカニズムは電気抵抗に基づいています。高抵抗材料で作られた特殊な発熱体に大電流が流されます。
この電流の流れに対する抵抗により、発熱体は非常に高温になり、この現象はジュール熱として知られています。
メカニズム:間接的な熱伝達
これらの発熱体からの強い熱は、炉内の材料に伝達されます。これは、放射、対流、および伝導の組み合わせによって起こります。
本質的に、炉はチャンバーの雰囲気と壁を加熱し、それが次にターゲット材料を加熱します。これは間接的な加熱プロセスです。
主な特徴
抵抗炉は、導電性か否かにかかわらず、あらゆる種類の材料を加熱できる汎用性で知られています。一般的に、設計がよりシンプルで、初期費用も安価です。

誘導炉の仕組み
誘導加熱は、より高度で、的を絞った、効率的な方法であり、熱エネルギーが材料に供給される方法を根本的に変えます。
原理:電磁誘導
誘導炉は、強力なコイルを使用して急速に変化する磁場を生成します。導電性材料(鋼やグラファイトなど)がこの磁場内に置かれると、磁場は材料自体の中に電流を誘導します。
これらの小さな円形の電流は渦電流として知られています。
メカニズム:直接的な内部加熱
これらの渦電流に対する材料本来の抵抗により、内部から正確かつ迅速な熱が発生します。外部の発熱体は必要ありません。
熱はワークピースの内部で直接発生するため、周囲の空間を加熱するエネルギーの浪費がほとんどなく、プロセスは非常に高速で効率的です。
主な特徴
溶融金属の誘導加熱のユニークな利点は、磁場によって引き起こされる自然な撹拌作用です。これにより、機械的な撹拌装置なしで優れた温度均一性と合金混合が保証されます。
トレードオフの理解:徹底比較
適切な炉を選択するには、各加熱方法に固有の明確な利点と限界を理解する必要があります。
加熱速度と効率
誘導炉は、著しく高速でエネルギー効率に優れています。熱が内部で発生するため、目標温度に達するまでの時間が大幅に短縮され、環境へのエネルギー損失も少なくなります。
抵抗炉は、まず発熱体と炉全体のチャンバーを加熱する必要があるため、サイクルタイムが遅くなり、全体的な効率が低下します。
材料適合性
抵抗炉は普遍的です。その動作は材料の電気的特性に依存しないため、金属、セラミックス、ポリマー、複合材料を問題なく加熱できます。
誘導炉は専門家です。非常に効果的ですが、電気的に導電性のある材料しか加熱できません。
温度制御と均一性
どちらのタイプも高レベルの温度制御を実現できます。ただし、誘導炉の自然な撹拌効果は、溶融金属用途において優れた熱均一性を提供します。
抵抗炉では、高い均一性を達成するために雰囲気を循環させるファンが必要となることが多く、これが複雑さを増します。
コストと複雑さ
抵抗炉は一般的に複雑さが少なく、初期費用も低いです。そのメンテナンスは、多くの場合、生涯にわたってよりシンプルで安価です。
誘導炉はより複雑なシステムであり、洗練された電源と冷却システムが必要となるため、初期投資が高くなります。
アプリケーションに最適な選択をする
最終的な決定は、特定の材料、プロセス要件、および予算によって完全に導かれるべきです。
- 汎用性と初期費用の低さを最優先するなら:抵抗炉が優れた選択肢であり、さまざまな材料や用途に対応する信頼性の高い主力製品として機能します。
- 速度、エネルギー効率、導電性金属の処理を最優先するなら:誘導炉は、特に溶解、ろう付け、または高速熱処理において、比類のない性能を提供します。
- セラミックスのような非導電性材料を扱う場合:抵抗炉が唯一の実行可能な選択肢です。
- 溶融金属浴の自動撹拌が必要な場合:誘導炉に固有の電磁撹拌は、主要な運用上の利点です。
この加熱メカニズムの根本的な違いを理解することが、特定の熱処理タスクに最も効果的なツールを選択するための鍵となります。
要約表:
| 特徴 | 抵抗炉 | 誘導炉 |
|---|---|---|
| 加熱方法 | 間接(ジュール熱) | 直接(電磁誘導) |
| 材料適合性 | すべての材料(普遍的) | 電気伝導性材料のみ |
| 加熱速度と効率 | 遅い、低効率 | 速い、高効率 |
| 主な利点 | 汎用性、低い初期費用 | 速度、精度、自動撹拌(金属の場合) |
研究室の特定の材料やプロセスにどちらの炉が適しているか、まだお悩みですか?
KINTEKは、実験装置と消耗品を専門としています。当社の専門家が、金属の溶解、合金の熱処理、セラミックスの加工など、お客様の用途要件を分析し、性能、効率、予算のバランスが取れた最適な炉ソリューションを推奨します。
今すぐ当社の熱処理スペシャリストにご連絡ください。個別相談を通じて、適切な炉が研究室の生産性と成果をどのように向上させるかを発見してください。
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
- 1400℃実験室用高温管状炉(アルミナチューブ付き)
- 1700℃実験室用高温管状炉(アルミナチューブ付き)
- 縦型実験室管状炉
- 実験室用ラピッドサーマルプロセス(RTP)石英管炉
- 実験室用1800℃マッフル炉



















