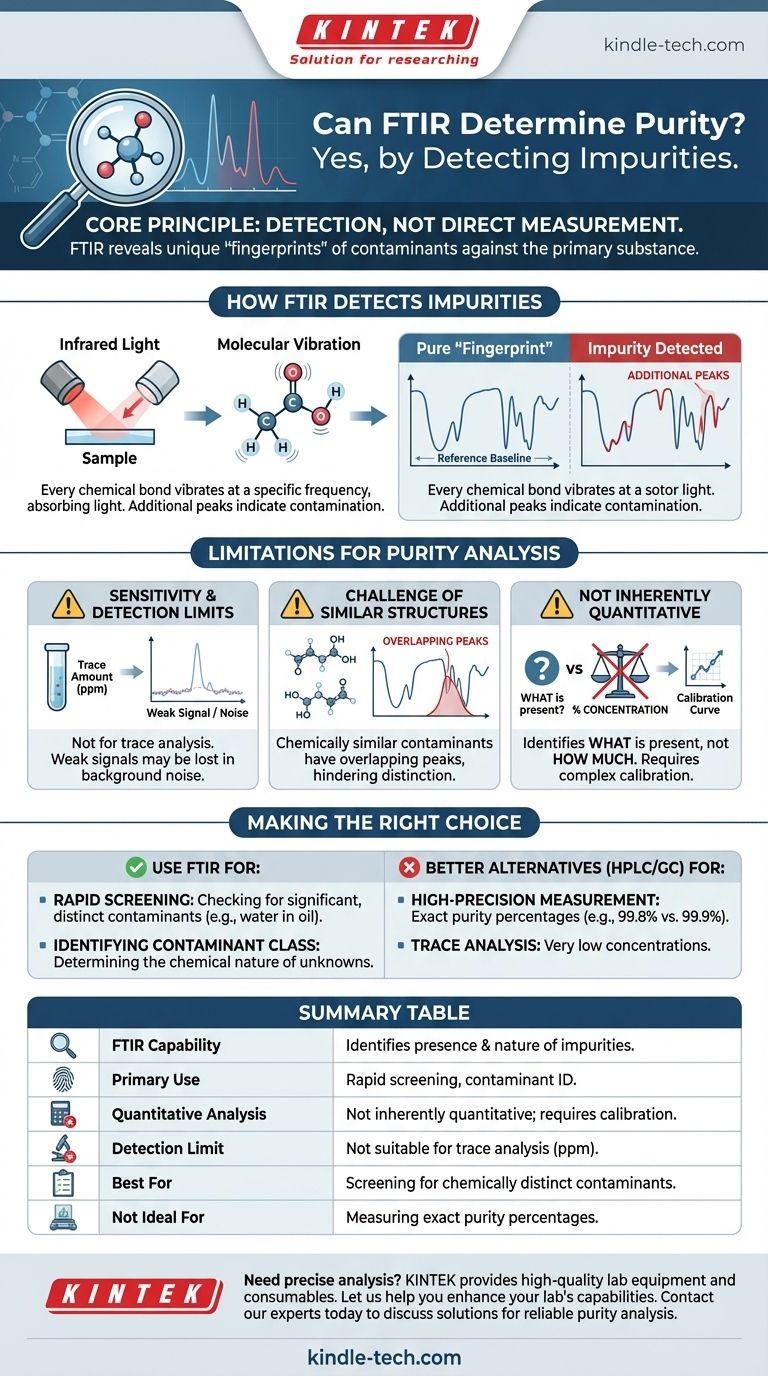
はい、FTIRは純度の評価に使用できますが、多くの人が期待するのとは異なる動作をします。特に高純度レベルでは、主成分の直接的なパーセンテージを提供するというよりも、不純物の存在とその化学的性質を特定することに優れています。
基本原理は、直接測定ではなく検出です。FTIRは、汚染物質の固有のスペクトル「フィンガープリント」を明らかにすることによって純度を評価します。その有効性は、不純物の化学的シグネチャが主要物質の背景に対して明確で検出可能であるかどうかに完全に依存します。
FTIRによる不純物の検出方法
FTIR、すなわちフーリエ変換赤外分光法は、サンプルに赤外光を照射し、異なる周波数でどれだけの光が吸収されるかを測定することによって機能します。このプロセスは、固有の化学的フィンガープリントとして機能するスペクトルを提供します。
分子振動の原理
分子内のすべての化学結合(C-H、O-H、C=Oなど)は特定の周波数で振動します。その周波数に一致する赤外光が結合に当たると、エネルギーが吸収されます。
FTIR分光法はこれらの吸収をマッピングし、サンプル中に存在する特定の化学結合に対応するピークのプロットを作成します。
純粋な「フィンガープリント」の確立
既知の純粋な物質の場合、得られるFTIRスペクトルは、一貫性があり認識可能なパターンであり、しばしばその「フィンガープリント」と呼ばれます。この参照スペクトルが純度分析のベースラインとして機能します。
汚染物質ピークの特定
不純物は、単に別の化学物質です。サンプル中に存在する場合、その固有の化学結合も赤外光を吸収します。
これらの吸収は、純粋な物質の参照フィンガープリントには存在しない追加のピークとしてスペクトルに現れます。これらの予期せぬピークの存在は、汚染の直接的な兆候です。

純度分析における限界の理解
強力ではありますが、FTIRは純度測定のための万能な解決策ではありません。その限界を理解することは、それに頼る前に不可欠です。
感度と検出限界
FTIRは一般的に微量分析には適していません。不純物が非常に低い濃度(例えば、百万分率)で存在する場合、その吸収シグナルはスペクトルのバックグラウンドノイズから区別するには弱すぎる可能性があります。
類似構造の課題
汚染物質が主成分と化学的に非常によく似ている場合(例えば、類似の溶媒や構造異性体)、それらの赤外吸収ピークは大きく重なる可能性があります。これにより、不純物のシグナルを主成分のフィンガープリントから区別することが困難または不可能になることがあります。
本質的に定量的ではない
そのままの状態では、FTIRは何が存在するかを示しますが、どれだけ存在するかを必ずしも示しません。不純物の濃度またはパーセンテージを決定するには、より複雑な定量分析を実行する必要があります。これには、不純物の既知の濃度の標準を使用して校正曲線を作成する必要があり、時間がかかる場合があります。
目的に合った適切な選択をする
その強みが目標と一致する場合に、純度分析にFTIRを使用してください。高精度な作業には、他の手法が優れています。
- 主な焦点が重大な汚染の迅速なスクリーニングである場合: FTIRは、既知の物質が化学的に異なる物質(例:オイル中の水の確認)で汚染されていないかを確認するための、優れた迅速な方法です。
- 主な焦点が未知の汚染物質の性質を特定することである場合: FTIRは、不純物として作用している化合物のクラスを決定するための強力なツールです。
- 主な焦点が正確な純度パーセンテージ(例:99.8%対99.9%)を測定することである場合: 高速液体クロマトグラフィー(HPLC)やガスクロマトグラフィー(GC)などの手法が業界標準であり、はるかに適切です。
結局のところ、FTIRは純度評価と汚染物質の特定のための貴重なツールですが、真の定量的純度分析の直接的な代替品ではありません。
要約表:
| 側面 | FTIRの能力 |
|---|---|
| 主な用途 | 不純物の存在と化学的性質を特定する。 |
| 定量分析 | 本質的に定量的ではない。濃度には校正が必要。 |
| 検出限界 | 微量分析(例:百万分率)には一般的に適さない。 |
| 最適な用途 | 重大で化学的に異なる汚染物質の迅速なスクリーニング。 |
| 不向きな用途 | 正確な純度パーセンテージ(例:99.8%対99.9%)の測定。 |
実験室サンプルに対して正確な分析が必要ですか?
FTIRは汚染物質を特定するための強力なツールですが、正確で定量的な結果を得るには、多くの場合、適切な機器と専門知識が必要です。KINTEKは、特定の分析課題に対応するための高品質なラボ機器と消耗品を提供することを専門としています。
ラボの能力向上をお手伝いします。 当社の専門家に今すぐお問い合わせいただき、お客様のニーズについてご相談の上、信頼できる純度分析に最適なソリューションを見つけてください。
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
- 多様な用途に対応する高性能ラボ用撹拌機
- 高度な科学および産業用途向けのカスタマイズ可能な高圧反応器
- 実験室用高圧水平オートクレーブ蒸気滅菌器
- ラボ用多機能小型速度調整水平メカニカルシェーカー
- 実験用スクエアラボプレス金型



















