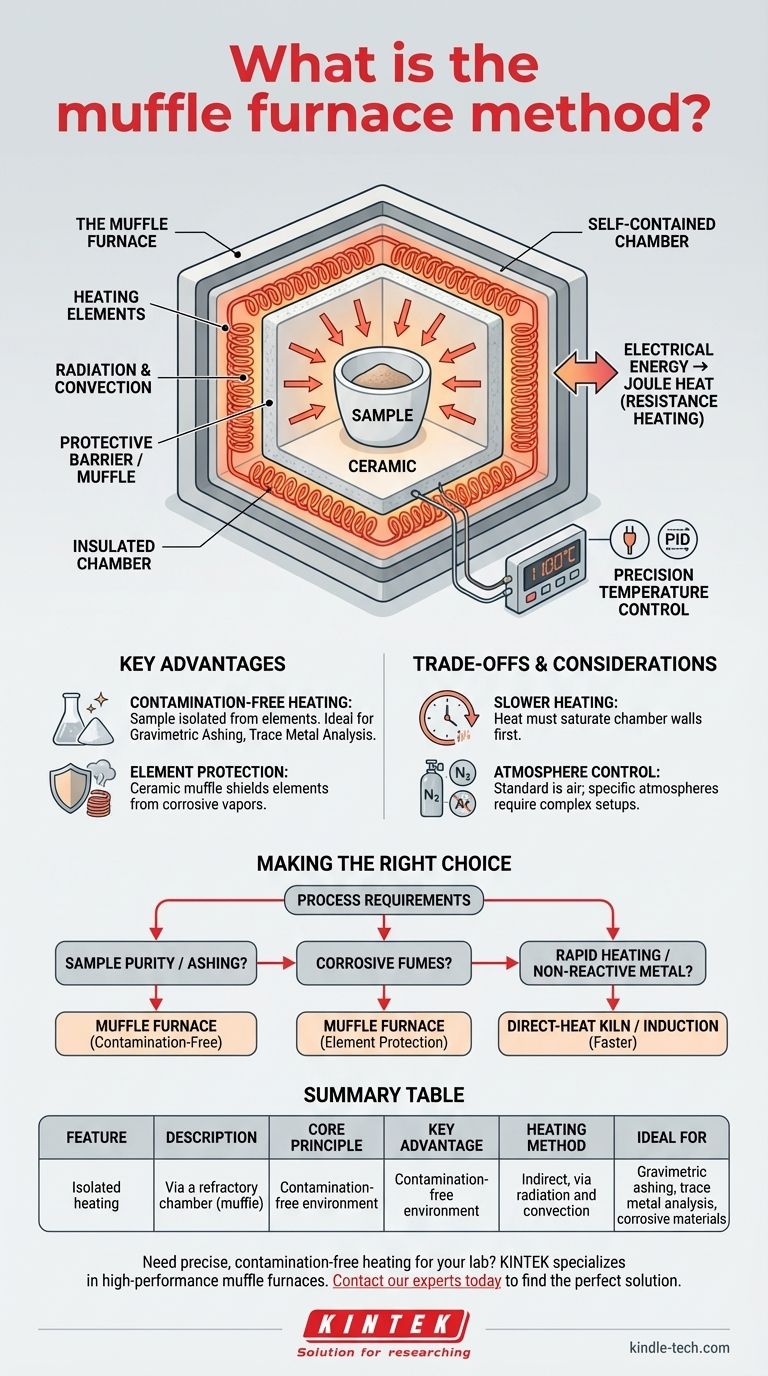
マッフル炉法は、加熱される材料が加熱要素や潜在的な汚染物質から物理的に隔離される高温加熱技術です。これは、クリーンで制御された均一な熱環境を保証する、自己完結型の断熱チャンバー、すなわち「マッフル」内で実現されます。
マッフル炉の決定的な特徴は、単に高温に達する能力ではなく、保護バリアを使用することです。この隔離により、相互汚染を防ぎ、サンプルを熱源から、また熱源をサンプルから保護します。
マッフル炉がいかにして隔離された加熱を実現するか
マッフル炉は、電気エネルギーを封じ込められた放射熱に変換するという、シンプルでありながら非常に効果的な原理で動作します。この設計は、研究および産業用途におけるその主要な機能の中核をなします。
基本原理:抵抗加熱
最新のマッフル炉の熱源は、電気抵抗によって生成されるジュール熱です。電流は、通常ニクロムなどの材料で作られた高抵抗の加熱コイルに通されます。
電気がこれらのコイルを通過するのに抵抗するため、エネルギーが失われ、それが激しい熱として放出されます。
「マッフル」の役割
歴史的に、マッフルは燃料焚き炉内に配置され、サンプルを炎から保護するための物理的なセラミックボックスでした。現代の電気炉では、チャンバー全体がマッフルとして機能します。
このチャンバーは、耐熱性の高い耐火材料(セラミックなど)で構成されています。これは、エネルギー効率のために熱を閉じ込め、サンプルを加熱要素から隔離するという2つの重要な機能を果たします。
熱伝達と均一性
加熱要素はマッフルチャンバーの壁を加熱します。これらの熱い壁は、主に対流と放射によって内部のサンプルに熱を伝達します。
この間接的な方法により、サンプルはすべての側面から均等に加熱され、材料試験や灰化における再現性のある結果に不可欠な、優れた温度均一性が提供されます。
精密な温度制御
最新の炉では、熱電対を使用して内部温度を正確に測定します。この情報はPIDコントローラー(比例・積分・微分)に送られます。
PIDコントローラーは、多くの場合、静かで信頼性の高い動作のためにソリッドステートリレーを使用して、加熱要素に送られる電力を正確に調整します。これにより、炉はわずかな変動で特定の温度を維持できます。

主な利点とトレードオフの理解
マッフル炉を選択することは、その隔離された設計に直接関連する明確な利点と、他の加熱方法と比較した場合の限界を理解することを含みます。
主な利点:汚染のない加熱
サンプルが加熱要素に接触することがないため、汚染のリスクは事実上排除されます。
これにより、クリーンな燃焼除去が必要な重量分析灰化や、外部の不純物が結果を損なう可能性のある微量金属分析などの用途で、マッフル炉は不可欠となります。
主な利点:要素の保護
マッフル設計は逆の働きも果たし、サンプルから加熱要素を保護します。
腐食性のガスや蒸気を放出する材料を加熱する場合、セラミックマッフルはシールドとして機能し、加熱コイルの寿命を大幅に延ばします。
一般的な誤解:加熱速度
マッフル炉は高温を維持する効率は高いですが、その加熱速度は、誘導炉や直火炉などの直接加熱方法よりも遅くなる可能性があります。
熱がサンプルに放射される前に、まずチャンバーの壁を飽和させる必要があり、わずかな熱遅延が生じます。
考慮事項:雰囲気制御
標準的なマッフル炉は、空気の入口と排気口を介して、空気の存在下でサンプルを加熱します。
特定の雰囲気(窒素やアルゴンなど)または真空下での加熱が用途で必要な場合は、特別で大幅に複雑な炉が必要になります。
用途に合わせた適切な選択
適切な加熱方法の選択は、特に純度、サンプルの反応性、温度均一性に関して、プロセスの特定の要件に完全に依存します。
- 主な焦点がサンプルの純度と灰化である場合: 汚染のない環境であるため、マッフル炉が決定的な選択肢となります。
- 主な焦点が腐食性のヒュームを放出する材料の加熱である場合: 装置を保護し、その寿命を確保するためにマッフル炉は不可欠です。
- 主な焦点が非反応性金属の急速な高温加熱である場合: よりシンプルで直接的な加熱キルンや誘導炉の方が、より速く、より費用対効果の高い解決策となる可能性があります。
結局のところ、マッフル炉法は、正確で均一でクリーンな高温熱処理を必要とするすべての人にとっての標準です。
要約表:
| 特徴 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 基本原理 | 耐火チャンバー(マッフル)による隔離された加熱 |
| 主な利点 | サンプル用の汚染のない環境 |
| 加熱方法 | 間接的、放射と対流による |
| 最適用途 | 重量分析灰化、微量金属分析、腐食性材料の加熱 |
ラボで正確で汚染のない加熱が必要ですか?
KINTEKは、サンプルの純度と温度均一性が重要な用途向けに設計された高性能マッフル炉を専門としています。当社の装置は、重量分析灰化、材料試験などの信頼性の高い結果を保証します。
当社の専門家に今すぐお問い合わせして、お客様の研究所のニーズに最適なソリューションを見つけてください。
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
よくある質問
- ラボ用オーブンの特徴は何ですか?研究室の精密で均一な加熱を確保
- 三元重整触媒に雰囲気制御マッフル炉が必要なのはなぜですか?焼成プロセスをマスターしましょう。
- 高温マッフル炉またはチューブ炉は、触媒の熱水エージングにどのように利用されますか?専門家による分析
- 鋼被覆の研究における実験室用マッフル炉の用途は何ですか?専門家による腐食分析
- NbTiVZr合金の評価におけるマッフル炉の主な機能は何ですか?高温原子力耐久性試験
- マッフル炉を使用する際にどのような注意を払うべきですか?研究室での安全な高温処理を確保する
- イルメナイト焙焼における高温マッフル炉の機能とは?鉱物の反応性を今日解き放つ
- Li6PS5Clの調製において、炉はどのような役割を果たしますか?硫化物電解質結晶化のマスター



















