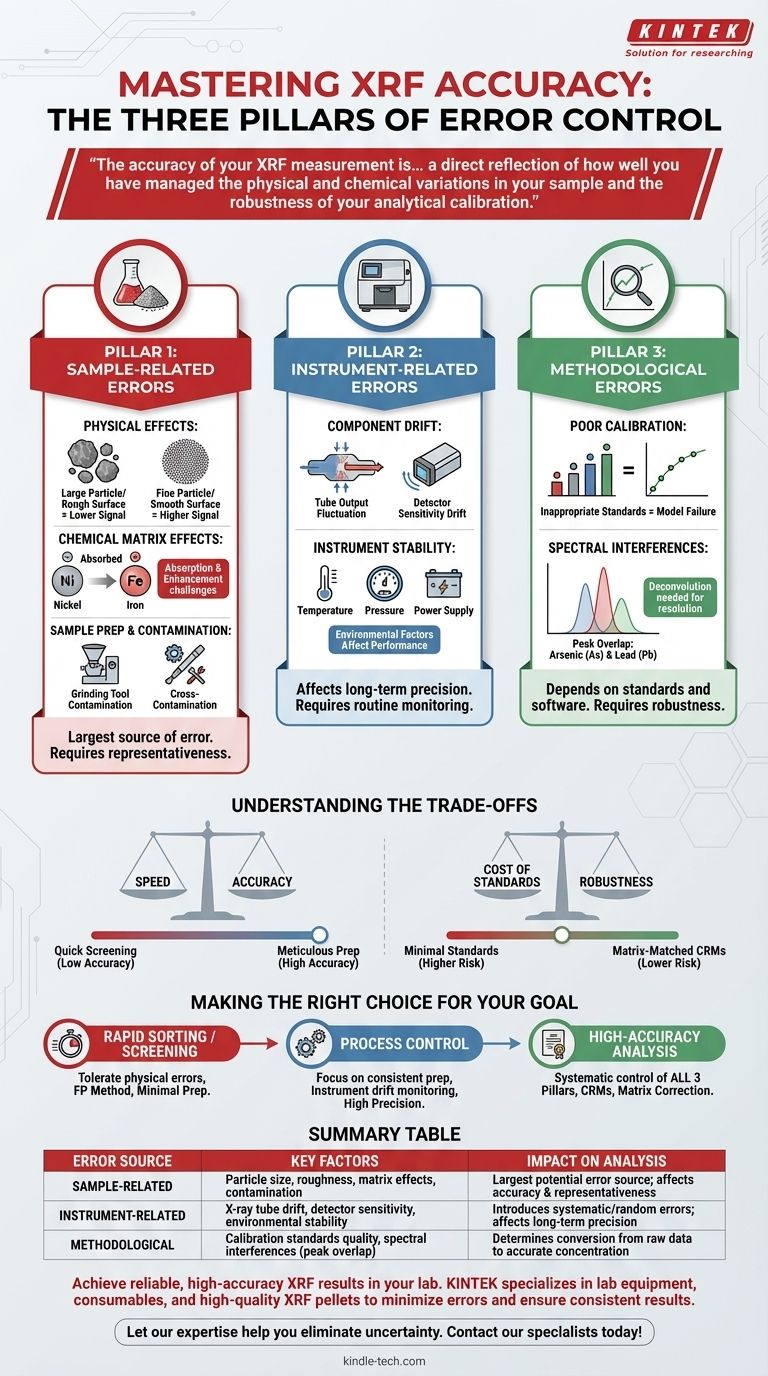
X線蛍光分析(XRF)において、誤差は3つの主要な領域から発生します。サンプル自体(物理的および化学的特性)、装置のハードウェアと安定性、および使用されている分析方法またはキャリブレーションです。前処理中のサンプル汚染などの要因は重要ですが、真に正確な結果は、これら3つの領域すべての変数を制御することにかかっています。
XRF測定の精度は、分光計の品質だけでなく、サンプルの物理的および化学的変動をいかにうまく管理し、分析キャリブレーションがいかに堅牢であるかを直接反映しています。
XRF誤差の3つの柱
信頼性の高い結果を得るためには、潜在的な不正確さがどこで発生するかを理解する必要があります。これらの原因は3つの異なるカテゴリに分類できます。
柱1:サンプル関連の誤差
これはしばしば最大の誤差源となります。分光計は提示されたサンプルしか測定できません。サンプルがバルク材料の真の代表でない場合、結果は不正確になります。
物理的効果
サンプルの物理的性質は、X線信号に劇的に影響を与えます。主な要因には、粒子サイズ、表面粗さ、およびサンプルの均一性が含まれます。
一般的に、細かい粒子は粗い粒子よりも強い蛍光信号を生成します。不均一な粉砕や粗い表面は、重大で予測不可能な誤差につながる可能性があります。
化学マトリックス効果
これは、サンプル中の他の元素が、測定しようとしている元素からのX線をどのように吸収または増強するかを指します。これはXRFにおける根本的な課題です。
たとえば、高濃度の鉄はニッケルからの蛍光を強く吸収し、ニッケルが実際よりも低濃度に見えることがあります。これらの効果は数学的に補正する必要があります。
サンプル前処理と汚染
サンプルの前処理方法は、重要な管理点です。ここで導入された誤差は元に戻せません。
前述のように、粉砕装置からの汚染は異物を導入する可能性があります。同様に、使用するたびに前処理ツールを徹底的に洗浄しないと、サンプル間の相互汚染が発生する可能性があります。

柱2:装置関連の誤差
最新のXRF分光計は非常に安定していますが、完璧ではありません。ハードウェアの変動は、分析に系統的またはランダムな誤差を導入する可能性があります。
コンポーネントのドリフト
最も重要な2つのコンポーネントであるX線管と検出器は、時間の経過とともに性能が変化する可能性があります。
X線管の出力強度は変動する可能性があり、検出器の感度は温度変化や経年劣化によりドリフトする可能性があります。これらの変化は通常ゆっくりであり、定期的な監視で管理できます。
装置の安定性
周囲温度、気圧(一部のシステムでは)、および電源の安定性などの要因は、分光計の性能に影響を与える可能性があります。
装置の制御された環境を維持することは、高精度で長期的な分析結果を達成するために不可欠です。
柱3:方法論的およびキャリブレーションの誤差
完璧なサンプルと安定した装置があったとしても、最終的な結果は分析方法とキャリブレーションの品質に完全に依存します。
不適切なキャリブレーション
キャリブレーションは、生のX線強度を元素濃度に変換する数学モデルです。このモデルは、作成に使用された標準物質の品質にのみ依存します。
未知のサンプルの化学マトリックスと一致しない不十分または不適切なキャリブレーション標準物質を使用することは、主要な分析誤差の主な原因です。
スペクトル干渉
場合によっては、2つの異なる元素の特性X線ラインが非常に近接しているため、検出器がそれらを分離できないことがあります。これはピークの重なりとして知られています。
たとえば、ヒ素のKα線は鉛のKβ線と重なります。これらのピークを数学的にデコンボリューションし、各元素の正確な結果を報告するには、洗練されたソフトウェアが必要です。
トレードオフの理解
すべての誤差源を制御することは、時間と費用がかかる場合があります。重要なのは、準備と分析の厳密さを特定の目標に合わせることです。
速度 vs. 精度
未処理のサンプルに対する迅速な「ポイントアンドシュート」分析は、単純な材料識別やスクリーニングには十分かもしれません。
しかし、このアプローチは精度を犠牲にし、品質管理や規制遵守には全く不適切です。これらの場合、綿密なサンプル前処理(粉砕やペレット化など)は不可欠です。
標準物質のコスト vs. 堅牢性
堅牢なキャリブレーションを作成するには、広範囲の高品質でマトリックスに適合した認証標準物質が必要であり、これらは高価になる可能性があります。
最小限の標準物質を使用したり、「タイプ標準化」(工場出荷時のキャリブレーションを1つまたは2つのローカルサンプルで調整する)に依存したりすることは安価ですが、サンプルが標準物質から逸脱した場合に誤差のリスクが高まります。
目標に応じた適切な選択
分析戦略は、答える必要がある質問によって決定されるべきです。
- 主な焦点が迅速な材料選別またはスクリーニングの場合: 物理的効果による誤差を許容し、簡単な基本パラメータ(FP)法を使用することで、サンプル前処理を最小限に抑えることができます。
- 主な焦点が既知の材料タイプを用いたプロセス制御の場合: 主な関心事は精度であるため、非常に一貫したサンプル前処理と定期的な装置ドリフト監視に焦点を当てます。
- 主な焦点が認証または研究のための高精度分析の場合: 綿密なサンプル前処理、キャリブレーション用の認証標準物質、およびマトリックス補正ソフトウェアを使用するなど、3つの柱すべてに体系的に対処する必要があります。
最終的に、XRFで精度を達成することは、体系的な管理の訓練であり、潜在的な誤差源を理解することがそれらを排除するための第一歩です。
要約表:
| 誤差源 | 主な要因 | 分析への影響 |
|---|---|---|
| サンプル関連 | 粒子サイズ、表面粗さ、化学マトリックス効果、汚染 | 最大の潜在的な誤差源。結果の精度と代表性に影響 |
| 装置関連 | X線管のドリフト、検出器の感度、環境安定性 | 系統的またはランダムな誤差を導入。長期的な精度に影響 |
| 方法論的 | キャリブレーション標準物質の品質、スペクトル干渉(ピークの重なり) | 生データから正確な濃度値への変換を決定 |
研究室で信頼性の高い高精度XRF結果を達成しましょう。
正確な分析への道筋は、サンプル、装置、およびメソッド全体で変数を制御することを必要とします。KINTEKは、研究室のニーズに応える高品質のXRFペレット、プレス、およびアクセサリーを提供し、サンプル前処理の誤差を最小限に抑え、一貫した結果を保証するように設計されています。
当社の専門知識が不確実性の排除を支援します。 今すぐ当社の専門家にお問い合わせください。お客様の特定のアプリケーションについて話し合い、分析目標をどのようにサポートできるかをご説明します。
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
- 実験室用試験ふるいおよびふるい機
- 三次元電磁ふるい分け装置
- 実験室用滅菌器 ラボオートクレーブ パルス真空リフティング滅菌器
- PTFEピンセット用カスタムPTFEテフロン部品メーカー
- 液晶ディスプレイ自動タイプ用実験室滅菌器ラボオートクレーブ縦型圧力蒸気滅菌器


















