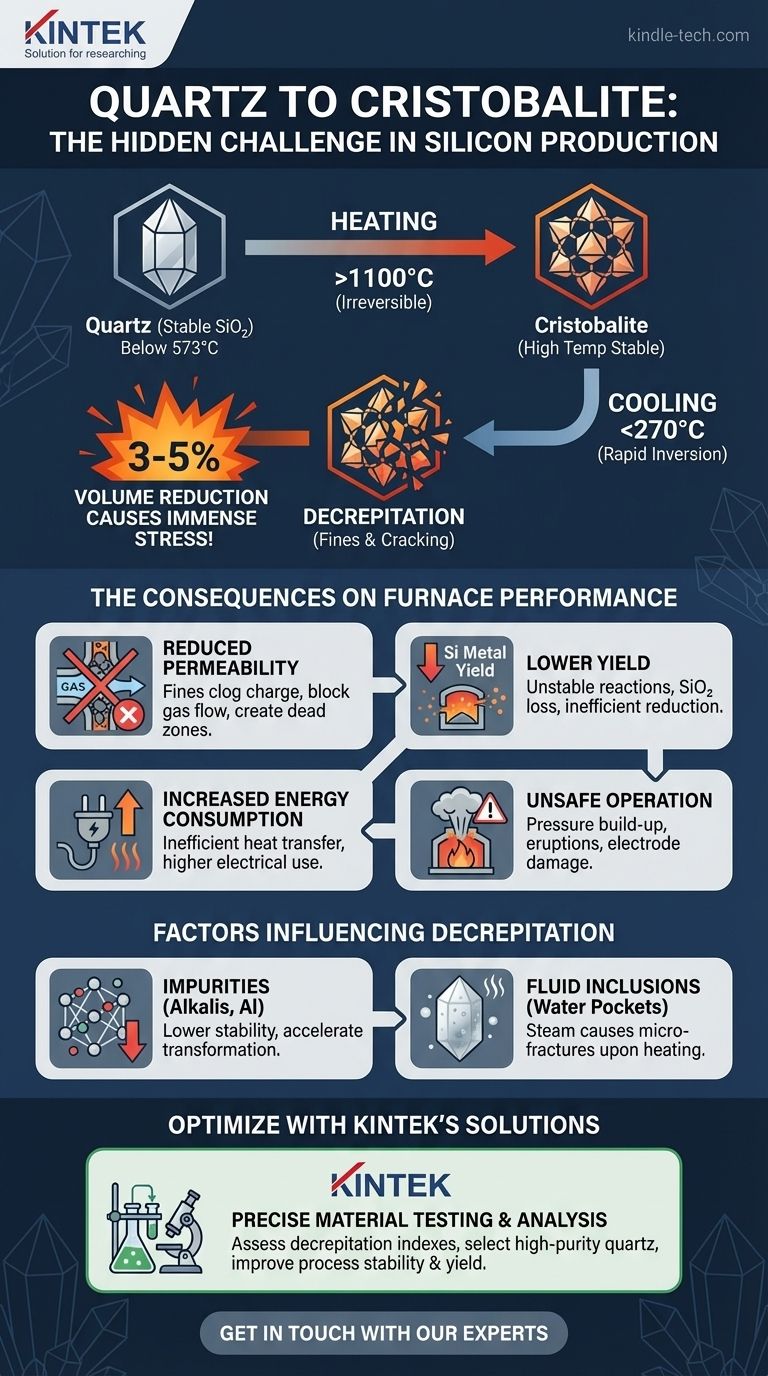
本質的に、シリコン炉での石英の加熱は、二酸化ケイ素(SiO₂)の異なる結晶形であるクリストバライトへの不可逆的な相変態を開始させます。この変態、特にクリストバライトが冷却される際に起こる急激な体積変化は、原材料の機械的不安定性の主要な原因であり、炉の効率、安全性、および全体的なシリコン収率に直接影響を与えます。
シリコン生産に石英を使用する上での中心的な課題は、加熱そのものではなく、冷却サイクルによる結果です。クリストバライトへの変態は、冷却時に材料を破砕させ、微細な粒子を生成し、製錬プロセス全体を混乱させる構造的な「記憶」をもたらします。
根本的な変態:石英からクリストバライトへ
石英の挙動を理解するには、シリコン炉の極端な熱の下でそれが不活性ではないことを認識することから始まります。その結晶構造は深遠で永続的な変化を遂げます。
石英とは?
石英は、常温常圧下で安定な二酸化ケイ素(SiO₂)の結晶形です。573°C以下ではα-石英として存在し、この温度を超えると可逆的にβ-石英に転移します。この初期の転移は、わずかな構造的変化を伴うだけです。
不可逆的な高温変化
炉内の温度が約1100°Cを超えると、石英構造はゆっくりと不可逆的に再配列し始め、非常に高温で安定なSiO₂の多形であるクリストバライトに変化します。別の相であるトリディマイトも形成されることがありますが、この工業的文脈ではクリストバライトがより重要で一般的な変態生成物です。
クリストバライトが主要な役割を果たす理由
一度形成されたクリストバライトは、冷却しても石英に戻ることはありません。これは、炉の上部ゾーンで高温に加熱された石英の塊がもはや石英ではなく、クリストバライトの塊になっていることを意味します。この新しい材料は、全く異なる物理的特性を持っています。

重大な問題:クリストバライトの転移
クリストバライト形成の最も重大な結果は、ピーク温度時ではなく、炉装入物内の冷却期間中に発生します。
高温クリストバライトと低温クリストバライト
石英と同様に、クリストバライトにも2つの形態があります。高温β-クリストバライト(約270°C以上で安定)と低温α-クリストバライトです。これら2つの形態間の転移は急速で可逆的です。
不安定性の原因:突然の体積変化
β-クリストバライトが約270°C以下に冷却されると、瞬時にα-クリストバライトに転移します。この転移には、3〜5%の突然かつ大幅な体積減少が伴います。この急速な収縮は、材料内部に巨大な内部応力を発生させます。
結果:破砕(Decrepitation)
α-βクリストバライト転移によって引き起こされる内部応力は、材料が耐えられないほど大きすぎることがよくあります。その結果、破砕(decrepitation)が発生します。これは、石英の塊が激しくひび割れ、破砕し、より小さな破片や微細な粒子に分解することです。それは、材料が内部から自らを粉砕するようなものだと考えてください。
破砕がシリコン生産に与える影響
微細粒子の生成は些細な問題ではありません。それは、シリコン生産に使用されるサブマージアーク炉の性能と安定性を根本的に低下させます。
炉の透過性への影響
シリコン炉は、炉床で発生した高温のCOガスが上方に流れ、下降する装入物を予熱・反応させる良好な透過性に依存しています。破砕による微細粒子は、大きな塊間の隙間を詰まらせ、この透過性を劇的に低下させます。
これにより、ガスの分布が悪くなり、ガス流量が過剰な「チャネル」と、ガス流量が少なすぎる「デッドゾーン」が生じます。
反応性と収率への影響
微粉は収率に2つの悪影響を及ぼします。第一に、チャネル内の激しいガス流は、微細なSiO₂粒子を炉外に直接吹き飛ばし、原材料の直接的な損失となります。
第二に、予測不能な装入物の動きとガス流は、安定した反応ゾーンを乱し、SiO₂からシリコン金属への還元を非効率にし、プロセス全体の収率を低下させます。
エネルギー消費の増加
ガスの分布が悪いと、熱伝達が非効率になります。炉全体で必要な温度を維持するためにより多くのエネルギーが必要となり、電力消費と運用コストが増加します。
不安定で危険な操業
ガスの流れが遮断されると、炉装入物内のポケットに圧力が蓄積することがあります。この閉じ込められたガスが突然放出されると、「噴出」や「吹き出し」を引き起こし、炉の操業が非常に不安定になり、電極に損傷を与える可能性があり、作業員にとって重大な安全上の危険が生じます。
トレードオフの理解:すべての石英が同じではない
特定の石英源の破砕傾向は、重要な品質パラメータです。これは、材料の純度と内部構造に大きく影響されます。
不純物の役割
石英結晶格子内の不純物、特にアルカリ(カリウムやナトリウムなど)やアルミニウムは、フラックスとして機能します。これらはクリストバライトへの変態のエネルギー障壁を下げ、より速く、より低い温度で変態が起こるようにし、破砕の程度を増加させます。
流体包有物の影響
「乳白色」または不透明な石英には、微細な流体包有物、つまり閉じ込められた水の小さなポケットが充満しています。加熱されると、この水は高圧蒸気に変わり、内部から微細な亀裂を生成します。これにより構造が弱くなり、破砕の影響が著しく悪化します。高純度で透明な石英は一般的に性能が優れています。
熱安定性の評価
これらの要因により、石英の「熱安定性」または「破砕指数」は、原材料選択の重要な指標となります。これは通常、石英のサンプルを加熱して炉の状態をシミュレートし、生成される微細材料の量を測定するラボテストによって決定されます。
石英の選択でプロセスを最適化する
石英の変態を深く理解することで、主要な原材料を管理することにより、反応的な問題解決から積極的なプロセス制御へと移行できます。
- 炉の安定性と収率の最大化が主な焦点である場合: 実証済みの低い破砕指数と最小限の流体包有物含有量を持つ高純度石英の調達を優先してください。
- 変動する原材料供給の管理が主な焦点である場合: 定期的な破砕テストを実施して石英のロットを分類し、一貫した予測可能な装入物挙動を維持するために戦略的にブレンドしてください。
- エネルギーコストの削減が主な焦点である場合: 破砕しやすい石英の使用を最小限に抑えることで、良好な装入物透過性を確保してください。これにより、ガスの分布と熱伝達効率が直接向上します。
SiO₂源の挙動を習得することは、安定した、効率的で、収益性の高いシリコン生産操業の基盤となります。
要約表:
| 段階 | 主な変化 | Si生産への主な影響 |
|---|---|---|
| 加熱(>1100°C) | 石英からクリストバライトへの不可逆的な変態。 | 冷却時の材料の不安定性の舞台を設定する。 |
| 冷却(<270°C) | 3〜5%の体積減少を伴う急速なα-βクリストバライト転移。 | 破砕(激しい破砕)を引き起こし、微細粒子を生成する。 |
| 炉の操業 | 微粉が装入物を詰まらせ、透過性を低下させ、ガスの流れを妨げる。 | 収率を低下させ、エネルギー消費を増加させ、危険な状態を作り出す。 |
原材料の挙動を習得することで、安定した効率的なシリコン生産を実現しましょう。 加熱下での石英の変態は、炉の性能において重要な要素です。KINTEKは、精密な材料試験と分析のための高純度ラボ機器と消耗品を提供しています。当社のソリューションは、石英の破砕指数を正確に評価し、最大の収率と操業安全性のために原材料の選択を最適化するのに役立ちます。シリコン生産の研究開発と品質管理におけるお客様の特定のニーズをサポートする方法について、今すぐお問い合わせください。
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
- 1400℃実験室用高温管状炉(アルミナチューブ付き)
- 縦型実験室管状炉
- 石英管付き1200℃分割管状炉 ラボ用管状炉
- 実験室用ラピッドサーマルプロセス(RTP)石英管炉
- 1700℃実験室用高温管状炉(アルミナチューブ付き)



















