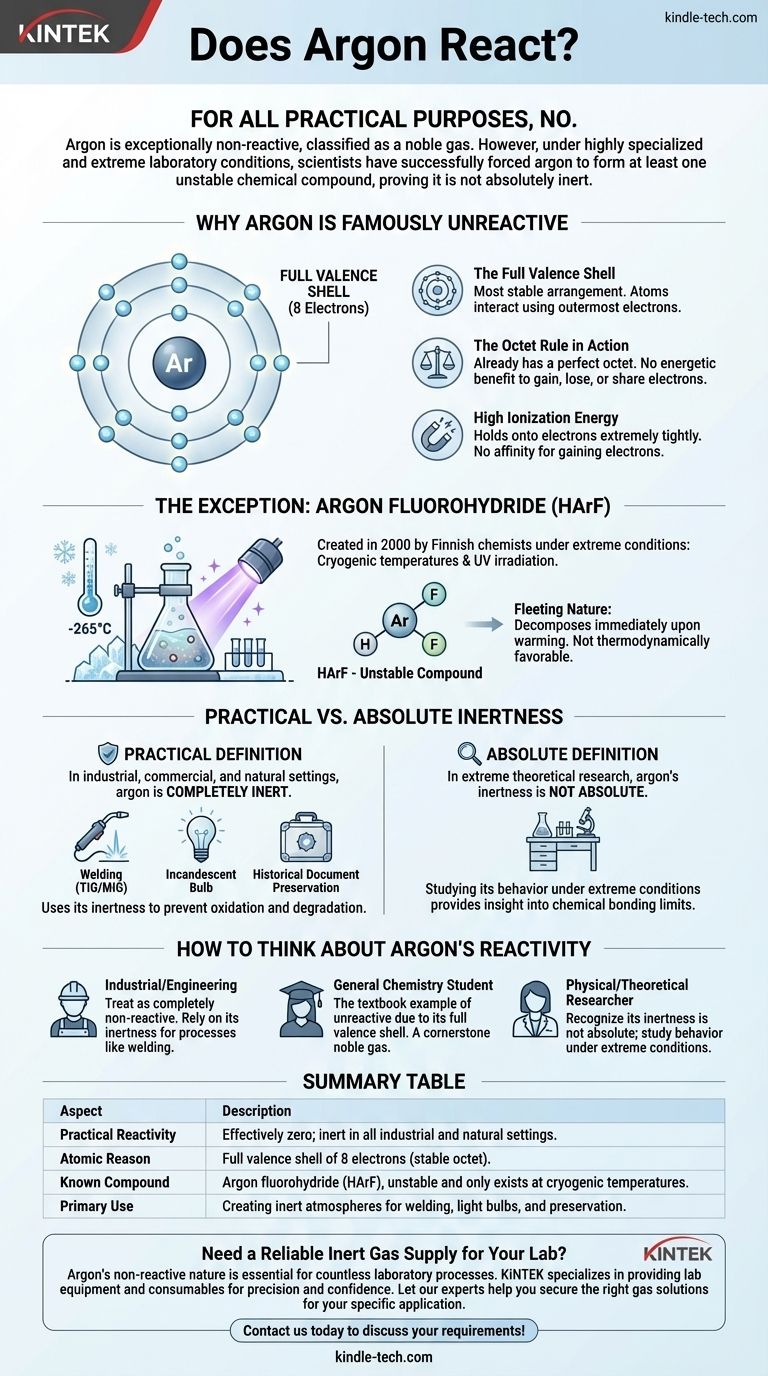
実用上は、いいえ。アルゴンは非常に反応性が低く、そのため希ガスに分類されています。しかし、高度に特殊化された極限的な実験条件下では、科学者たちはアルゴンに少なくとも1つの不安定な化合物を形成させることに成功しており、それが完全に不活性ではないことを証明しています。
重要なのは、元素の「反応性」が単純なイエス・ノーの問題ではないということです。アルゴンの完璧な電子殻配置は、あらゆる自然または産業環境において不活性にしますが、極低温条件下で十分なエネルギーを与えれば、その非反応性を克服でき、化学結合の微妙な複雑さを明らかにします。
アルゴンが「不活性」として有名である理由
アルゴンがなぜ化学結合を非常に強く拒むのかを理解するには、その原子構造を見る必要があります。不活性であるという評判は恣意的なものではなく、その電子配置の直接的な結果です。
完全に満たされた最外殻
原子は、価電子として知られる最外殻電子を使って相互作用し、結合を形成します。
アルゴンは8つの価電子を持ち、その最外殻電子殻を完全に満たしています。これは原子が持つことができる最も安定した配置です。
「オクテット則」の働き
「オクテット則」は、原子が8つの電子からなる完全な最外殻を達成するために、電子を得たり、失ったり、共有したりする傾向があるという化学の基本的な原理です。
アルゴンはすでにこの完璧なオクテットを持っているため、他の原子と電子を得たり、失ったり、共有したりすることにエネルギー的な利点はありません。すでに理想的な低エネルギー状態にあるのです。
高いイオン化エネルギー
イオン化エネルギーとは、原子から電子を1つ取り除くのに必要なエネルギーです。アルゴンは非常に高いイオン化エネルギーを持っており、これは電子を極めて強く保持していることを意味します。
同様に、電子を得る親和性もありません。通常の状況下では、アルゴンが反応に関与する化学的な「動機」は単純に存在しないのです。
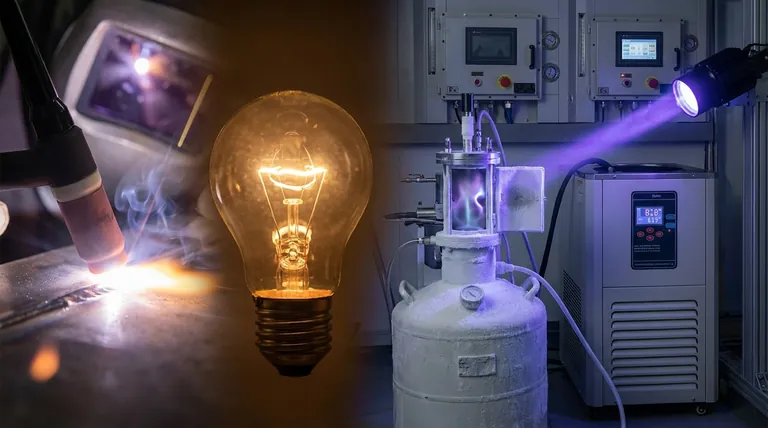

規則を証明する例外
何十年もの間、アルゴンは完全に不活性であると信じられていました。これは2000年にフィンランドの化学者チームが最初の既知の真のアルゴン化合物を生成したことで変わりました。
極限条件下での反応の強制
フッ化水素アルゴン (HArF) という化合物は、一般的な実験用ビーカーで作られたものではありません。
科学者たちは、アルゴンとフッ化水素の混合物を絶対零度に近い温度(約-265°Cまたは-445°F)で表面に凍結させ、その後、強力な紫外線で照射する必要がありました。この極限的なエネルギー入力が、反応を嫌がるアルゴン原子を一時的に結合させるのに十分でした。
アルゴン化合物の短命な性質
生成されたHArF化合物は信じられないほど不安定です。これらの極低温でのみ存在します。
わずかにでも温められると、弱い結合が切れ、すぐに別々のアルゴンとフッ化水素に分解します。これは、この化合物が熱力学的に有利ではなく、極度の低温によって「閉じ込められている」ためにのみ存在することを示しています。
実用的な不活性と絶対的な不活性
この発見は、2つの概念を区別することを私たちに強います。つまり、実用的な意味で真実であることと、絶対的、理論的な意味で真実であることです。
不活性の実用的な定義
あらゆる産業、商業、または自然環境において、アルゴンは完全に不活性です。空気、水、金属、または接触する他の物質と反応することはありません。
この実用的な不活性こそが、アルゴンを非常に価値あるものにしています。
これが用途にとって重要な理由
アルゴンの非反応性は、欠点ではなく特徴です。溶接(TIG/MIG)では、溶融金属の周りに不活性な「シールド」を作り、酸化や空気中のガスとの反応を防ぎ、クリーンで強力な溶接を保証します。
白熱電球では、アルゴン雰囲気によって高温のタングステンフィラメントが燃え尽きるのを防ぎます。歴史的文書の保存では、劣化を防ぐために酸素のない環境を提供します。
アルゴンの反応性について考える方法
アルゴンの化学的挙動をどのように見るかは、あなたの文脈によって決まります。この区別を理解することが、化学原理を正しく適用する鍵となります。
- 産業または工学の現場で働いている場合:アルゴンを完全に非反応性のガスとして扱ってください。その不活性は最も価値のある特性であり、溶接や製造などのプロセスで信頼できます。
- 一般化学の学生である場合:アルゴンは、完全な価電子殻を持つため、反応しない元素の教科書的な例であり、希ガスグループの基礎であることを理解してください。
- 物理化学または理論化学の研究者である場合:アルゴンの不活性は絶対的なものではなく、極限条件下でのその挙動を研究することは、化学結合の限界に関する貴重な洞察を提供することを認識してください。
最終的に、アルゴンが反応を極端に嫌うという性質は、科学的に興味深く、現実世界で非常に有用であるという両方の側面を持つ基本的な特性です。
要約表:
| 側面 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 実用的な反応性 | 実質的にゼロ。すべての産業および自然環境で不活性。 |
| 原子的な理由 | 8つの電子からなる完全な価電子殻(安定したオクテット)。 |
| 既知の化合物 | フッ化水素アルゴン (HArF)、不安定で極低温でのみ存在する。 |
| 主な用途 | 溶接、電球、保存のための不活性雰囲気の作成。 |
研究室に信頼できる不活性ガス供給が必要ですか?
アルゴンの非反応性は、制御された雰囲気の作成からデリケートな材料の取り扱いまで、数え切れないほどの実験室プロセスに不可欠です。一貫した高純度供給を確保することは、結果にとって極めて重要です。
KINTEKは、お客様が正確かつ自信を持って作業するために必要な実験装置と消耗品を提供することに特化しています。当社の専門家が、お客様の特定の用途に合った適切なガスソリューションを確保するお手伝いをいたします。
ビジュアルガイド
関連製品
- 10L 冷却循環器 クーリングウォーターバス 低温恒温反応槽
- リチウム電池用アルミニウム箔電流コレクタ
- ラボスケール真空誘導溶解炉
- 低温水冷タッチスクリーン振動超微粉砕機
- カスタムPTFEテフロン部品メーカー グラインディングボウル
よくある質問
- バイオ炭製造における高温雰囲気炉の機能とは?効果的な吸着剤のエンジニアリング
- 雰囲気炉とは?制御された環境での加熱ガイド
- FeAl/Al2O3/TiO2コーティングにおける雰囲気管炉の役割とは?高度な層合成のための専門家ガイド
- アルゴンは冷却に使用できますか?はい、化学的不活性が必要な特殊な用途であれば可能です。
- 触媒焼成における雰囲気炉の役割とは?脱硝触媒の高性能化を実現する
- なぜ焼鈍炉に窒素が使用されるのですか?優れた金属品質のために酸化と脱炭を防ぐためです
- 不活性ガス雰囲気熱処理とは何ですか?金属を酸化や脱炭から保護する方法
- 高純度水素雰囲気炉の作業メカニズムとは?タングステン焼結効率をマスターする














